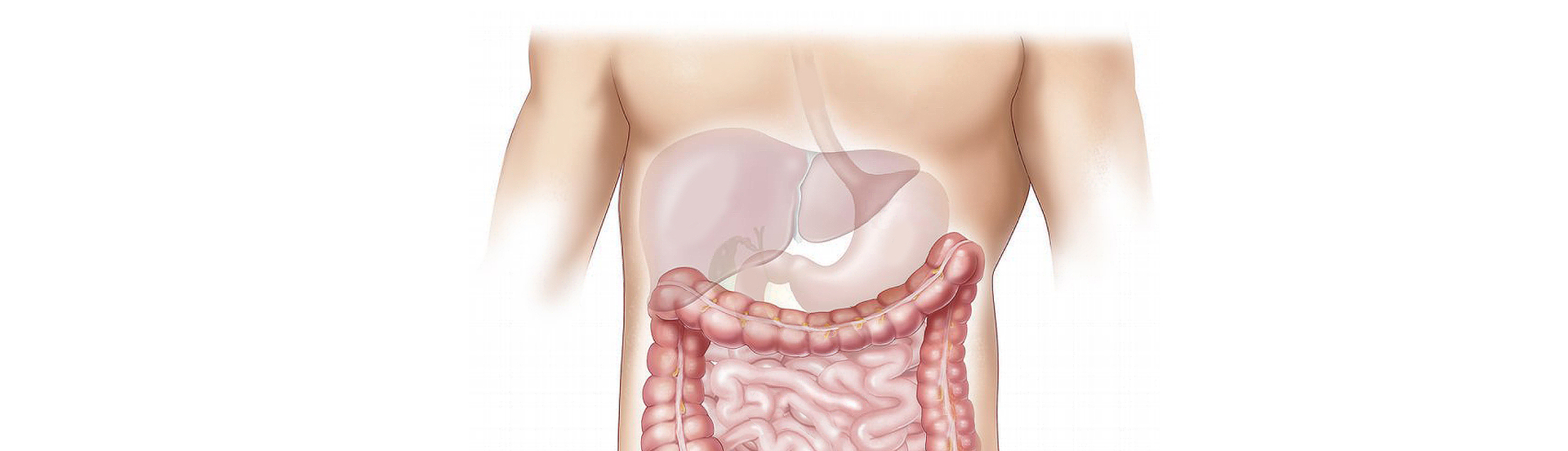
Nurturing Your Body’s Lifesaver
synthesis and assembly of proteins
production of bile, a substance which digests fats
helps to manage energy stores and contributes to childhood growth
breaks down toxic substances
plays a role in blood pressure management
Common symptoms of liver disease
Feeling of Dizziness • Stroke • Redness and itchiness of eyes • Short temperedness and constant irritation • Tension and pain in the back • Hypochondriac pain • Loss of flexibility of tendons and ligaments • Depression • Mood Swings • Headache • Jaundice • Appetite • Digestion • Problem of skin • Allergy • Tinnitus • Ticks, Spasms and Tremors • Sudden SeizuresList of Liver Disease 1. Acetaminophen Toxicity 2. Alcoholic Liver Disease 3. Liver Cirrhosis 4. Primary Liver Cancer 5. Liver Cysts 6. Liver Fibrosis 7. Fatty Liver Disease 8. Hepatitis
What Are the Symptoms of Hepatitis A?
Hepatitis A is inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus. When symptoms occur, they may include:
- Jaundice (condition causing yellow eyes and skin, dark urine)
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
Children often have hepatitis A with few symptoms. A person can spread the hepatitis A virus about a week before his or her symptoms appear and during the first week of having symptoms. People with no symptoms can also spread the virus. Hepatitis B is a virus that infects the liver: . Most adults who get it have it for a short time and then get better. This is called acute hepatitis B. Sometimes the virus causes a long-term infection, called chronic hepatitis B. Over time, it can damage your liver. Babies and young children infected with the virus are more likely to get chronic hepatitis B. You can have hepatitis B and not know it. You may not have symptoms. If you do, they can make you feel like you have the flu. But as long as you have the virus, you can spread it to others. It’s caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is spread through contact with the blood and body fluids of an infected person. You may get hepatitis B if you:
- Have sex with an infected person without using a condom.
- Share needles (used for injecting drugs) with an infected person.
- Get a tattoo or piercing with tools that weren’t sterilized.
- Share personal items like razors or toothbrushes with an infected person.
A mother who has the virus can pass it to her baby during delivery. Medical experts recommend that all pregnant women get tested for hepatitis B. If you have the virus, your baby can get shots to help prevent infection with the virus. You cannot get hepatitis B from casual contact such as hugging, kissing, sneezing, coughing, or sharing food or drinks. Many people with hepatitis B don’t know they have it, because they don’t have symptoms. If you do have symptoms, you may just feel like you have the flu. Symptoms include: Hepatitis C is a disease caused by a virus that infects the liver. In time, it can lead to permanent liver damage as well as cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. Many people don’t know that they have hepatitis C until they already have some liver damage. This can take many years. Some people who get hepatitis C have it for a short time and then get better. This is called acute hepatitis C. But most people who are infected with the virus go on to develop long-term, or chronic, hepatitis C. Although hepatitis C can be very serious, most people can manage the disease and lead active, full lives. Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is spread by contact with an infected person’s blood. You can get hepatitis C if:
- You share needles and other equipment used to inject illegal drugs. This is the most common way to get hepatitis C in the United States.
- You had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992. As of 1992 in the United States, all donated blood and organs are screened for hepatitis C.
- You get a shot with a needle that has infected blood on it. This happens in some developing countries where they use needles more than once when giving shots.
- You get a tattoo or a piercing with a needle that has infected blood on it. This can happen if equipment isn’t cleaned properly after it is used.
- In rare cases, a mother with hepatitis C spreads the virus to her baby at birth, or a health care worker is accidentally exposed to blood that is infected with hepatitis C.
CIRRHOSIS OF LIVER
Cirrhosis is a very serious condition in which scarring damages the liver. The liver is a large organ that is part of the digestive system. It does a wide range of complex jobs that are vital for life. For example, the liver:
Makes many important substances, including bile to help digest food and clotting factors to help stop bleeding.
- Filters poisons from the blood.
- Breaks down (metabolizes) alcohol and many drugs.
- Controls the amounts of sugar, protein, and fat in the bloodstream.
- Stores important vitamins and minerals, including iron.
When a person has cirrhosis, scar tissue replaces healthy tissue. This scar tissue prevents the liver from working as it should. For example, the liver may stop producing enough clotting factors, which can lead to bleeding and bruising. Bile and poisons may build up in the blood. Scarring can also cause high blood pressure in the vein that carries blood from the intestines through the liver (portal hypertension). This can lead to severe bleeding in the digestive tract and other serious problems. Cirrhosis can be deadly. But early treatment can help stop damage to the liver. Cirrhosis can have many causes. Some of the main ones include: Less common causes of cirrhosis include severe reactions to medicines or long-term exposure to poisons, such as arsenic. Some people have cirrhosis without an obvious cause. You may not have symptoms in the early stages of cirrhosis. As it gets worse, it can cause a number of symptoms,.
Liver Cancer
What is liver cancer?
Liver cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the tissue of the liver and is the growth and spread of unhealthy cells in the liver. Cancer that starts in the liver is called primary liver cancer. Cancer that spreads to the liver from another organ is called metastatic liver cancer. What are some liver cancer symptoms? Early liver cancer often doesn’t cause symptoms. When the cancer grows larger, people may notice one or more of these common symptoms:
- Pain in the upper abdomen on the right side
- A lump or a feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen
- Swollen abdomen (bloating)
- Loss of appetite and feelings of fullness
Weight loss - Weakness or feeling very tired
- Nausea and vomiting
- Yellow skin and eyes, pale stools, and dark urine from jaundice
- Fever